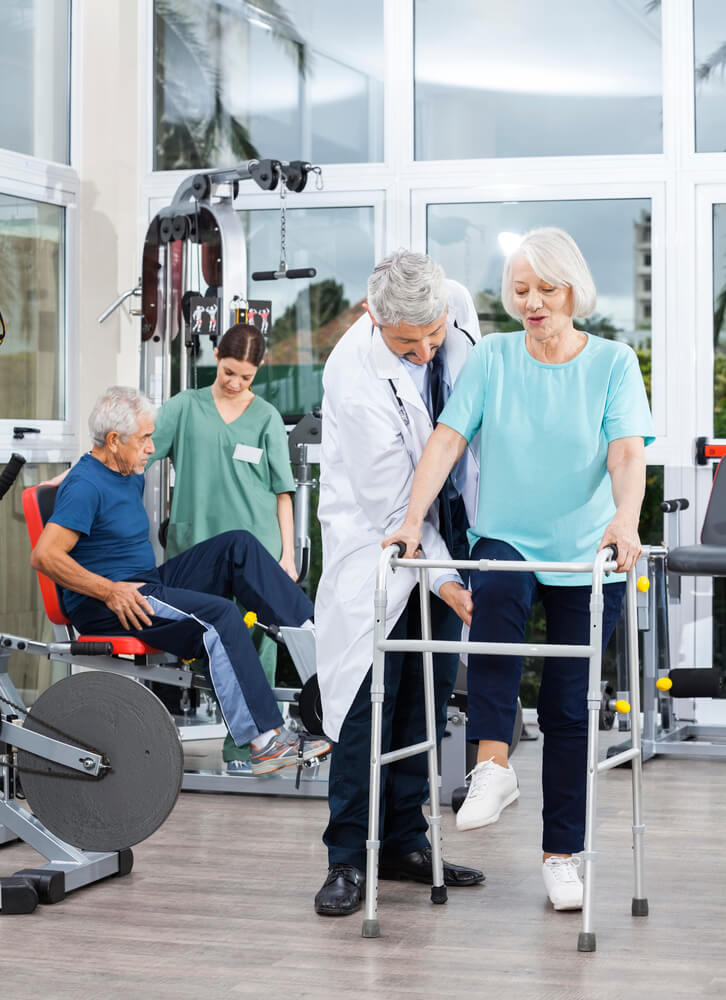
A stroke is a traumatic event that can cause lasting damage, including cognitive decline. Cognitive decline can range from mild to severe and can affect a person’s ability to think, reason, and remember. But there is hope. The brain has an incredible ability to rewire itself, and with the right coping strategies, individuals can recover and thrive after a stroke. In this blog post, we’ll explore the science behind the brain’s resilience and how it can be harnessed to promote recovery from post-stroke cognitive decline. From implementing healthy lifestyle changes to relying on technology, we’ll cover a range of strategies that can help individuals not only recover but also improve their cognitive abilities after a stroke.
1. Understanding post-stroke cognitive decline
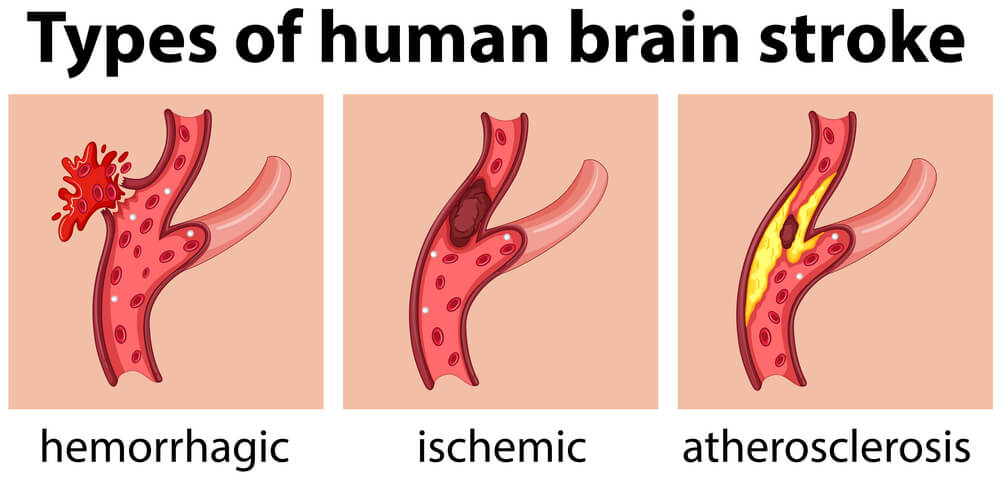
Post-stroke cognitive decline is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects a significant number of stroke survivors. When someone experiences a stroke, the flow of blood to the brain is disrupted, leading to damage in various areas. While physical impairments are commonly associated with stroke, the cognitive effects can be just as impactful, if not more so.
Post-stroke cognitive decline refers to the changes in cognitive function that occur after a stroke. These changes can manifest in various ways, including difficulties with memory, attention, problem-solving, language, and executive functions. The severity and specific symptoms can vary from person to person, depending on the location and extent of the brain damage.
It is important to understand that post-stroke cognitive decline is not a uniform condition. Each individual’s experience will be unique, making it crucial to tailor interventions and coping strategies to their specific needs. Some individuals may experience subtle changes in cognitive function, while others may face more significant challenges that impact their daily lives.
It’s worth noting that post-stroke cognitive decline can have a profound emotional impact on stroke survivors and their loved ones. Frustration, anxiety, and depression are common emotions that may arise as a result of these cognitive changes. Therefore, providing support and understanding to those affected is essential in their journey towards recovery.
By understanding the nature of post-stroke cognitive decline, we can begin to explore strategies and interventions that can help individuals regain cognitive function and improve their overall quality of life. From cognitive rehabilitation exercises to lifestyle modifications, there are various approaches that can be employed to foster brain resilience and enhance cognitive abilities.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the rewiring and coping strategies that can aid in unlocking the brain’s resilience after stroke and mitigating the impact of cognitive decline. With the right knowledge, resources, and support, individuals can navigate the challenges posed by post-stroke cognitive decline and work towards regaining their cognitive abilities.
2. Brain plasticity and resilience and its potential for rewiring
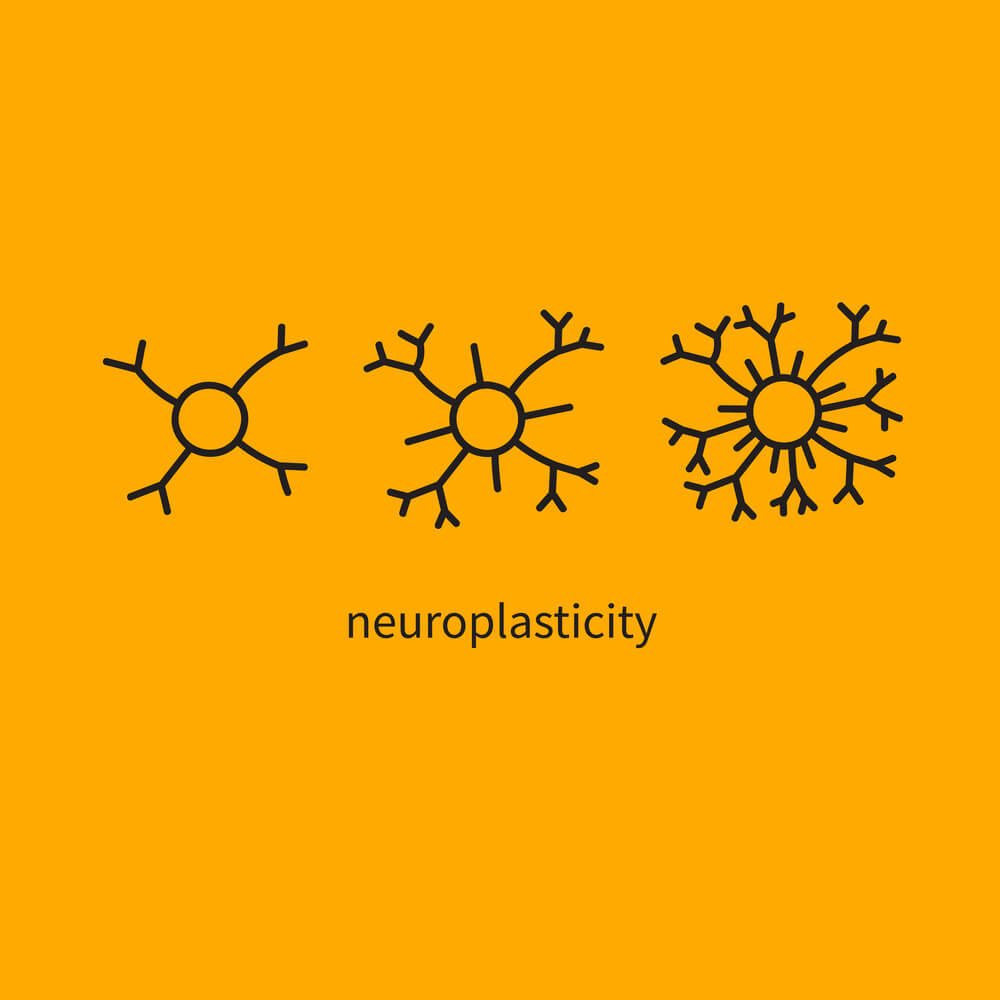
The human brain is a remarkable organ with an extraordinary capacity for resilience. When faced with challenges such as post-stroke cognitive decline, the brain has the potential to rewire itself and regain lost cognitive functions. This phenomenon, known as neuroplasticity, allows the brain to adapt and create new neural pathways to compensate for the areas affected by stroke.
Neuroplasticity is not limited to a specific age or time frame. It can occur at any stage of life, offering hope for stroke survivors who may experience cognitive difficulties. The brain’s ability to rewire itself is a testament to its remarkable plasticity and adaptability.
Through targeted rehabilitation exercises, cognitive therapies, and engaging in mentally stimulating activities, stroke survivors can harness the power of neuroplasticity to retrain their brains and improve cognitive function. These strategies involve repetitive exercises that focus on specific cognitive skills, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving.
The rewiring process may take time and patience, but the brain’s resilience and capacity for change provide a glimmer of hope for those facing post-stroke cognitive decline. With dedication and the right strategies, stroke survivors can tap into the brain’s inherent ability to rewire itself, fostering recovery and enhancing overall cognitive well-being.
3. Common cognitive challenges after a stroke
After experiencing a stroke, individuals often face various cognitive challenges that can significantly impact their daily lives. Understanding these common challenges is crucial in developing effective strategies to cope with and overcome them.
One of the most common cognitive challenges after a stroke is memory loss. This can range from mild forgetfulness to more severe forms of amnesia. Individuals may struggle to remember recent events, names, or even familiar faces. Additionally, they may find it difficult to retain new information or follow conversations.
Another common cognitive challenge is attention and concentration difficulties. Many stroke survivors struggle with maintaining focus and may get easily distracted. They may have trouble multitasking or following complex instructions, making it challenging to complete tasks that require sustained attention.
Language and communication difficulties are also prevalent after a stroke. Aphasia, a language impairment, can affect the ability to speak, understand, read, or write. This can lead to difficulties in expressing oneself, finding the right words, or comprehending written or spoken language.
Executive function deficits are another cognitive challenge that stroke survivors often encounter. These deficits can affect problem-solving, organization, planning, and decision-making abilities. Individuals may struggle with managing time, setting goals, initiating and completing tasks, and adapting to changes.
Visuospatial and perceptual difficulties are also common. Stroke survivors may have difficulty judging distances, perceiving depth, or recognizing familiar objects or faces. They may struggle with spatial orientation, making it challenging to navigate or perform activities that require coordination and spatial awareness.
It is essential to recognize that these cognitive challenges can vary from person to person and may manifest differently in each individual. However, understanding these common difficulties can serve as a starting point in developing personalized coping strategies and interventions to promote cognitive recovery and enhance overall quality of life for stroke survivors.
4. Coping strategies for memory and attention deficits
Coping with memory and attention deficits after experiencing a stroke can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it is possible to improve these cognitive functions and regain a sense of normalcy in daily life.
One of the most effective coping strategies for memory and attention deficits is to establish routines and habits. By creating a structured daily schedule, individuals can reduce cognitive overload and enhance their ability to remember and focus on tasks. This can be achieved by setting specific times for activities such as meal preparation, exercise, and leisure activities. Additionally, using reminder systems such as alarms, calendars, or smartphone apps can help individuals stay organized and remember important appointments or tasks.
Another helpful coping strategy is the use of external memory aids. These aids can include physical tools like notebooks, sticky notes, or whiteboards to jot down important information, appointments, or to-do lists. Digital tools such as smartphone apps, voice recorders, or reminder apps can also be beneficial in keeping track of important details and tasks. By relying on these external memory aids, individuals can offload some cognitive demands and free up mental space for other activities.
Engaging in cognitive exercises and activities specifically designed to target memory and attention can also be highly beneficial. These exercises can include puzzles, memory games, word associations, or even computer-based brain training programs. Regular participation in these activities can help stimulate neural pathways, improve cognitive functions, and enhance memory and attention abilities over time.
Furthermore, practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can aid in coping with memory and attention deficits. Stress and anxiety can exacerbate cognitive difficulties, so incorporating activities like meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga into daily routines can promote relaxation, reduce stress levels, and improve overall cognitive function.
It is essential to remember that coping strategies may vary from person to person, and it is crucial to tailor them to individual needs and abilities. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, such as occupational therapists or neuropsychologists, can provide personalized strategies and support for managing memory and attention deficits effectively.
By implementing these coping strategies, individuals can unlock the brain’s resilience and improve their cognitive abilities after experiencing a stroke. With time, patience, and consistent effort, it is possible to enhance memory and attention, regain independence, and lead a fulfilling life post-stroke.
5. Cognitive rehabilitation techniques for language and communication difficulties
Cognitive rehabilitation techniques play a crucial role in helping individuals recover and regain their language and communication skills after experiencing post-stroke cognitive decline. Language and communication difficulties can significantly impact a person’s ability to interact, express themselves, and participate in everyday activities. Therefore, it is essential to focus on specific strategies that can help rewiring the brain and improving these cognitive functions.
One effective technique is speech therapy, which involves working with a speech-language pathologist who specializes in post-stroke rehabilitation. These professionals can assess the individual’s specific language and communication challenges and develop personalized therapy plans. Through various exercises and activities, they aim to improve speech clarity, word retrieval, sentence formation, and overall communication skills.
Additionally, augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) methods can be employed to assist individuals who struggle with verbal communication. AAC involves the use of tools and techniques such as communication boards, electronic devices, or apps that facilitate communication through gestures, symbols, or text. These aids can be particularly helpful for individuals who have difficulty speaking or understanding spoken language.
Another aspect of cognitive rehabilitation is addressing reading and writing difficulties. Occupational therapists and specialized educators can work with individuals to improve their reading comprehension, writing skills, and overall literacy. This may involve exercises to enhance reading fluency, comprehension strategies, and adaptive technologies that assist with writing, such as word prediction software or speech-to-text tools.
Furthermore, memory and attention training can significantly benefit individuals experiencing cognitive decline. Through specific exercises and techniques, individuals can improve their ability to focus, sustain attention, and enhance memory recall. These interventions can include activities such as puzzles, memory games, attention-building exercises, and strategies like mnemonic devices or external memory aids.
It’s important to note that cognitive rehabilitation techniques should be tailored to each individual’s unique needs, abilities, and goals. A comprehensive assessment by a multidisciplinary team, including neurologists, speech-language pathologists, occupational therapists, and psychologists, can provide valuable insights into the most effective strategies for an individual’s specific challenges. Regular practice, consistency, and ongoing support from healthcare professionals and loved ones are crucial for achieving optimal results in rewiring the brain and improving language and communication abilities after post-stroke cognitive decline.
6. Assistive technologies for post-stroke cognitive decline
Assistive technologies have revolutionized the way we support individuals with post-stroke cognitive decline. These innovative tools and devices are designed to enhance cognitive functioning, improve independence, and promote overall well-being for stroke survivors.
One remarkable assistive technology is the use of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). BCIs enable individuals to control external devices using their brain signals, bypassing physical limitations. For post-stroke survivors experiencing motor impairments, BCIs offer a new way to communicate, control electronic devices, and even regain mobility through the use of exoskeletons or robotic limbs.
Another valuable assistive technology is the advent of wearable devices and mobile applications specifically tailored for cognitive rehabilitation. These tools provide personalized cognitive exercises and games that target areas such as memory, attention, language, and problem-solving. With real-time feedback and progress tracking, stroke survivors can engage in meaningful cognitive training in the comfort of their own homes, empowering them to take an active role in their recovery journey.
Furthermore, there are assistive technologies that support daily activities and memory management. Smart home automation systems, for instance, can be programmed to remind individuals about medication schedules, appointments, and important tasks. Voice-controlled virtual assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Apple’s Siri can provide verbal prompts and assistance, helping stroke survivors navigate their daily routines more independently.
It is important to note that the selection of assistive technologies should be based on individual needs and preferences. Occupational therapists and other healthcare professionals play a crucial role in assessing cognitive abilities, identifying functional goals, and recommending suitable assistive technologies that align with each person’s unique circumstances.
By harnessing the power of assistive technologies, individuals with post-stroke cognitive decline can unlock their brain’s resilience, regain independence, and enhance their quality of life. These transformative tools offer hope, empowerment, and endless possibilities for stroke survivors on their journey of rewiring and coping with cognitive challenges.
7. Lifestyle changes and habits to promote brain health
When it comes to promoting brain health and unlocking the brain’s resilience, making lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits can play a crucial role. These changes not only support overall well-being but also help in managing post-stroke cognitive decline effectively.
First and foremost, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is essential. Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can provide the brain with the necessary nutrients to function optimally. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals. Additionally, staying hydrated is vital for brain function, so ensure an adequate intake of water throughout the day.
Regular physical exercise is another lifestyle change that can greatly contribute to brain health. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, or yoga not only improves cardiovascular fitness but also enhances blood flow to the brain, promoting the growth of new nerve cells. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
To further support brain health, it is important to prioritize quality sleep. During sleep, the brain consolidates memories, repairs and rejuvenates itself. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night and establish a consistent sleep schedule to optimize cognitive function.
Managing stress is also crucial for brain health. Chronic stress can negatively impact the brain and contribute to cognitive decline. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation.
Engaging in mental stimulation is another habit that can help maintain cognitive function. Challenge your brain by learning new skills, solving puzzles, reading, or engaging in activities that require cognitive effort. This keeps the brain active and promotes neural connections.
Lastly, social interaction and maintaining strong social connections can have a positive impact on brain health. Engage in activities with friends, family, and community groups to stimulate the brain and promote emotional well-being.
By implementing these lifestyle changes and healthy habits, you can promote brain health, support the brain’s resilience, and effectively cope with post-stroke cognitive decline. Remember, small changes can make a big difference in unlocking the brain’s potential for recovery and overall well-being.
8. The role of physical exercise in cognitive recovery
Physical exercise plays a crucial role in cognitive recovery after a stroke. It not only promotes overall physical health but also stimulates the brain to rewire and rebuild neural connections that may have been damaged during the stroke.
Engaging in regular physical exercise has been shown to increase blood flow to the brain, which enhances the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen that are necessary for the brain’s optimal functioning. Furthermore, exercise promotes the release of growth factors in the brain, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports the growth and survival of neurons.
Studies have demonstrated that individuals who engage in consistent aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, experience improvements in cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and executive functioning. This is because aerobic exercise increases the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are crucial for cognitive processes.
Additionally, physical exercise can also have a positive impact on mood and mental well-being, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety that often accompany post-stroke cognitive decline. Regular exercise can boost self-esteem, improve sleep quality, and alleviate stress, all of which contribute to better cognitive functioning.
It is important to note that the type and intensity of exercise should be tailored to the individual’s abilities and guided by a healthcare professional. Engaging in a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and balance exercises can provide a well-rounded approach to cognitive recovery after a stroke.
In conclusion, physical exercise plays a vital role in rewiring the brain and promoting cognitive recovery after a stroke. By incorporating regular exercise into a post-stroke rehabilitation plan, individuals can enhance their cognitive functions, improve overall well-being, and unlock their brain’s resilience.
9. Emotional support and mental well-being after a stroke
Emotional support and maintaining mental well-being are crucial aspects of the recovery process after experiencing a stroke. The impact of a stroke extends beyond the physical realm, often causing emotional distress, anxiety, and depression in individuals. Recognizing and addressing these emotional challenges is essential in promoting overall well-being and facilitating the rewiring of the brain.
After a stroke, it is common for individuals to experience a range of emotions, including frustration, sadness, and a sense of loss. Connecting with a support system, whether it be family, friends, or a support group, can provide a crucial source of emotional support. Sharing experiences, concerns, and triumphs with others who have gone through similar situations can alleviate feelings of isolation and provide a sense of belonging.
In addition to seeking support from others, practicing self-care and engaging in activities that promote mental well-being is equally important. Engaging in hobbies, exercising, and practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation can help reduce stress and improve overall emotional health. It is also essential to communicate openly with healthcare professionals about any emotional challenges faced post-stroke, as they can provide guidance, resources, and potentially recommend therapy or counseling services to assist in navigating these difficulties.
Furthermore, it is essential to be patient and kind to oneself during the recovery process. Accepting that healing takes time and progress may be gradual is an important mindset to cultivate. Celebrating small victories and recognizing personal growth can help boost self-confidence and motivation.
Remember, the journey of recovery after a stroke is unique to each individual. Prioritizing emotional support and mental well-being alongside physical rehabilitation and cognitive exercises can significantly contribute to rewiring the brain and enhancing overall resilience. With the right support and strategies in place, individuals can navigate the challenges of post-stroke cognitive decline and unlock their brain’s incredible capacity for healing and adaptation.
10. Empowering stroke survivors to embrace their cognitive abilities
A stroke can have a profound impact on a person’s cognitive abilities, often leading to difficulties in memory, attention, and problem-solving. However, it is essential to empower stroke survivors to embrace their cognitive abilities and regain control over their lives.
One effective approach is to focus on the strengths and capabilities that remain after a stroke. Encouraging stroke survivors to identify and nurture their existing cognitive skills can provide them with a sense of accomplishment and motivation to continue their recovery journey. This could involve engaging in activities that exercise their cognitive abilities, such as puzzles, brain games, or learning new skills.
Another empowering strategy is to create a supportive environment that fosters independence and autonomy. Providing stroke survivors with opportunities to make decisions, solve problems, and engage in meaningful activities can help rebuild their confidence and sense of self-worth. It is crucial to acknowledge their efforts and celebrate small victories along the way, reinforcing their belief in their cognitive abilities.
Additionally, involving stroke survivors in their rehabilitation process can be empowering. Collaborating with healthcare professionals to set realistic goals and actively participating in therapy sessions can give them a sense of ownership over their recovery. By being actively involved, stroke survivors can better understand their progress and work towards improving their cognitive functioning.
Equally important is providing education and resources to stroke survivors and their caregivers. Educating them about the nature of post-stroke cognitive decline, coping strategies, and available support networks can empower them to navigate the challenges they may encounter. It is essential to emphasize that cognitive decline does not define their worth or potential and that there are ways to adapt and thrive despite the challenges.
Empowering stroke survivors to embrace their cognitive abilities goes beyond the physical recovery process. By focusing on strengths, creating a supportive environment, involving them in their rehabilitation, and providing education and resources, we can help unlock the brain’s resilience and empower stroke survivors to live fulfilling lives post-stroke.